Home | Education | Tendon Disorders | deQuervains Tendinitis
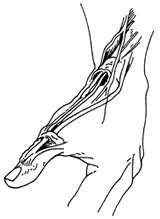
Figure 1: Swelling about the tendons to the base of the thumb results in painful motion.
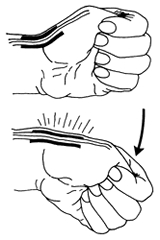
Figure 2: Finkelstein maneuver used to diagnose deQuervain's tendinitis.
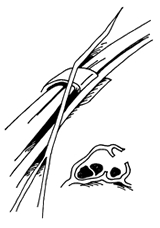
When symptoms are severe or do not improve, surgery may be recommended. The surgery opens the compartment (covering) to make more room for the irritated tendons (Figure 3). Normal use of the hand can usually be resumed once comfort and strength have returned. Dr. Smith can advise you on the best treatment for deQuervain’s tendinitis.
Dr. Smith provides a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach for the evaluation, treatment and care of deQuervain’s tendinitis.
Figure 3:Surgery opens the sheath over the inflamed tendons.
The information on this webpage is based on material from the American Society for Surgery of the Hand and is for educational purposes only.

deQuervain’s Tendinitis Treatment and Surgery
By Houston Hand Surgery Specialist & Orthopaedic Surgeon, Dr. Dean Smith
deQuervain’s tendinitis is a condition brought on by irritation or swelling of the tendons found along the thumb side of the wrist (Figure 1). The irritation causes the compartment (lining) around the tendon to swell, changing the shape of the compartment; this makes it difficult for the tendons to move as they should. The swelling can cause pain and tenderness along the thumb side of the wrist, usually noticed when forming a fist, grasping or gripping things, or turning the wrist.Figure 1: Swelling about the tendons to the base of the thumb results in painful motion.
What causes deQuervain’s Tendinitis?
The cause of deQuervain’s tendinitis is an irritation of the tendons at the base of the thumb. For example, awkward hand positions required by a new mother in caring for an infant is a common cause of this condition.Signs and Symptoms of deQuervain's
Pain over the thumb side of the wrist is the main symptom. The pain may appear either gradually or suddenly. It is felt in the wrist and can travel up the forearm. The pain is usually worse with use of the hand and thumb, especially when forcefully grasping things or twisting the wrist. Swelling over the thumb side of the wrist is noticed and may be accompanied by a fluid-filled cyst in this region. There may be an occasional “catching” or “snapping” when moving the thumb. Because of the pain and swelling, it may be difficult to move the thumb and wrist, such as in pinching. Irritation of the nerve lying on top of the tendon sheath may cause numbness on the back of the thumb and index finger.
Diagnosis of deQuervain's Tendinitis
A Finkelstein test is generally performed. In this test, the patient makes a fist with the fingers over the thumb. The wrist is then bent in the direction of the little finger (Figure 2). This test can be quite painful for the person with deQuervain’s tendinitis. Tenderness directly over the tendons on the thumb-side of the wrist is the most common finding, however.Figure 2: Finkelstein maneuver used to diagnose deQuervain's tendinitis.

Treatment of the deQuervain's Tendinitis
The goal is to relieve the pain caused by the irritation and swelling. In some cases, Dr. Smith may recommend resting the thumb and wrist by wearing a splint. Anti-inflammatory medication taken by mouth or injected into that tendon compartment may help reduce the swelling and relieve the pain. In some cases, simply not doing the activities that cause pain and swelling may allow the symptoms to go away on their own.When symptoms are severe or do not improve, surgery may be recommended. The surgery opens the compartment (covering) to make more room for the irritated tendons (Figure 3). Normal use of the hand can usually be resumed once comfort and strength have returned. Dr. Smith can advise you on the best treatment for deQuervain’s tendinitis.
Dr. Smith provides a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach for the evaluation, treatment and care of deQuervain’s tendinitis.
Figure 3:Surgery opens the sheath over the inflamed tendons.